1.
Adaptive
Optics
The jaw of a Venus flytrap is the
part of the plant where it captures its prey such as insects as shown in Figure
1. When an insect is drawn into the open jaws, it will tickles and stimulate
the trigger hairs on the inner surface of the open jaws. As soon as an insect
trigger two outgrowths in short succession, the open jaws will snap and traps
the insect. The speed at which the jaws trap the insect is approximately 100ms.
Figure
1: Open Jaws with Trigger Hair
It is hard for any insects to
escape the trap as the response speed of the trap is hard to beat. The response
speed of stimulation through its trigger hair enable the Venus flytrap to
capture its prey at high speed without fail. This is due to the fact that the
microscopic structure of inner surface of the jaws are made up of tiny lobes
and it has the ability to change shape from concave to convex at very high
speed of 100ms. Figure 2 shows the shape changing process of the lobe.
Figure
2: Shape Changing of Lobes
The shape changing process of
tiny lobes at high speed has been mimicked to create a complex lens where the
reflectivity of the surface will change to focus by itself. This complex lens
is known as adaptive lens which is implemented into adaptive optics method by
astronomers. Adaptive optics comprise of deformable mirrors which can be controlled
by computers to correct in real-time for distortion caused by the turbulence of
the earth’s atmosphere.
A large strong beam of laser will
be pointed to the targeted star as shown in Figure 3. The reflected light will
directed to the adaptive optics system to capture the targeted image as shown
in Figure 4.
Figure 3: Laser Emitted Towards
Targeted Star
Figure 4: Adaptive Optics System
As a result, unclear image of
stars captured through normal telescope can be converted to a sharper image by
eliminating distorted wavefront as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Images Captured With
and Without Adaptive Optics
2.
Morphing
Turbine
The leaf of the Venus flytrap
also known as the jaw which comes in a pair and it is mechanically connected to
each other. As the jaws experience inplane contraction or expansion the
curvature of the leave will experience change in shape as well. For example,
trapping and opening of the jaws will result in change of the jaw’s curvature.
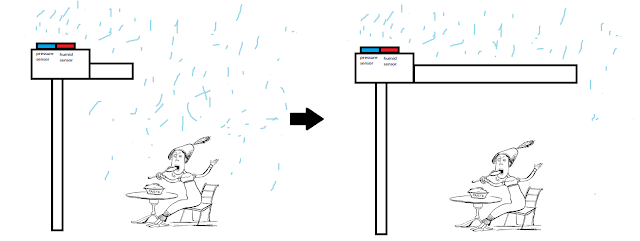
When the insect triggered the trap, water flows between the inner and outer
faces of the jaw, changing the curvature of the jaw in x direction as shown in
Figure 6. Conversely, as the jaws close and trap the insect the curvature
changes as shown in Figure 7.
Figure
6: Open State
Figure
7: Closed State
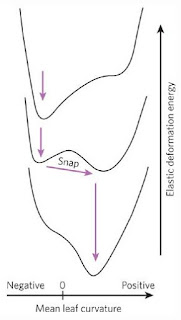
When the jaws are in open state,
it has negative curvature and maximum elastic deformation energy. On the other
hand, when the jaws are in closed state, it has positive curvature and minimum
elastic deformation energy. Plot of curvature and elastic deformation energy
for both states are shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8:
Curvature and Elastic Deformation Energy
The shape changing ability of
Venus flytrap in terms of curvature is mimicked and implemented into wind
turbine of wind power plant. The conventional turbine as shown in Figure 9 is
only able to generate movement when the wind is directed towards the correct
direction. The Venus flytrap inspired turbine is known as morphing turbine as
shown in Figure 10.
Figure 9:
Conventional Turbine
Figure
10: Morphing Turbine
The rotor blades of the morphine
turbine are made of smart material such as shape memory material which is able
to adapt environment conditions and changes its shape. Single element blades of
morphing turbine are stiff in structure and implement effective tailoring to
produce effective pitch and structure as shown in Figure 11.
Figure
11: Rotor Blades of Morphing Turbine
Regardless of any direction the
wind-blown towards the wind turbine, the blades of the wind turbine is able to
adapt the flow conditions and change its geometry. As a result, the morphing
turbine changes its blade to a more aerodynamic geometry which results the
turbine spinning with lesser resistance. Simple and low weight structure of the
morphine turbine blades is able to generate power from wind with high
efficiency. Cost per kilowatt of energy produced can be lowered, thus saving
electrical consumption and cost for major factory industries etc.
3.
Magnetic
Buttons
The jaws of the Venus flytrap are
able to capture and trap its prey such insects of various sizes. Average leaf
size of Venus flytrap can grow up to the range 3 cm to 8 cm as shown in Figure
12. If the growth of the plant is optimum, the leaf can reach up to the size of
13 cm which is almost the size of a human palm. Hence, a fully grown Venus flytrap
is able to trap and capture a medium sized frog as shown in Figure 13.
Figure
12: Leaf Size of Venus Flytrap
Figure
13: Frog captured by a Venus Flytrap
When a Venus flytrap captures its
prey, the jaws will shut tightly and form an air-tight seal to keep it
digestive fluid within the boundary and bacteria out. The jaws will concealed
and trap its prey, leaving the prey with no space for movement to escape. The flytrap
will devour its food and will open its jaws approximately 8 to 11 days later. Since
the shutting mechanism is effective as escaping from the trap by any prey is
difficult due to its tightly concealed jaws. The leaf shape which forms the shutting
mechanism of the Venus flytrap jaws is mimicked and applied as magnetic buttons
for clothing. As shown in Figure 14, the buttons are designed in the shape of
Venus flytrap jaws. Each pair of jaw consists of opposite poles of magnet
namely: North and South. The buttoning mechanism is shown in Figure 15.
Figure
14: Magnetic Buttons
Figure
15: Buttoning Mechanism
The Venus flytrap inspired button
allows easy and convenient buttoning and unbuttoning of shirt. Besides that,
the tightly concealment of the buttons ensure that the buttons are not detached
easily. Of course, the magnetic strength also reflects the attraction between
the buttons. However, the factor which ensure the button conceal tightly is the
contact surface area when the pair of button are attached together. The extra
surface areas are formed between the “teeth” of the jaws when the pair of jaws closes.
As a result, a higher surface area generates stronger magnetic strength which
ensures the buttons are firmly attached.